We are Manufacturer, Supplier, Exporter of Water Treatment Process, Physical Water Treatment Process, Chemical Water Treatment Process, Physio-Chemical (Conventional), Water Treatment Process, Biological Water Treatment Process, Dual Media Filters, Activated Carbon Filters, Water Softening Systems, Demineralization Process (DM Plant), Sewage Treatment Plant, Ultrafiltration System, from Pune, Maharashtra, India.
Impurities in Water
- Suspended Impurities
- Organic Impurities
- Dissolved Organic Impurities
- Dissolved Inorganic Impurities
- Dissolved Gased
Objectives of Water Treatment Process
- To remove color and odor from water.
- To remove the hardness of water.
- To remove the harmful microbes that cause diseases from water.
- To remove murkiness and turbidity of the water.
- To remove dissolved gases present in water.
- To make the water suitable for various purposes like drinking, industrial and many others as per the demand.
IMPURITIES |
RELATED PROBLEMS |
|
Dissolved Oxygen (ppm) |
Pitting Corrosion |
|
pH |
Corrosivity |
|
TSS (NTU / ppm) |
Fouling |
|
Total Hardness (ppm CaCO3) |
Scaling |
|
Sodium / Potassium (ppm) |
Corrosivity |
|
Chloride (ppm) |
Corrosivity |
|
Sulphate (ppm) |
Corrosivity / Scaling |
|
Total Alkalinity (ppm CaCO3) |
Scaling, Foaming |
|
Phenophthalene Alkalinity (ppm CaCO3) |
Scaling, Foaming, Corrosivity |
|
Silica (ppm) |
Scaling |
|
TDS / Organics (ppm, Conductivity) |
Foaming, Corrosivity |
The Processes Involved in Water Treatment
Following are the types of processes involved in the water treatment
- Sedimentation
- Filtration
- Dissolved Air Flotation
- Pre-chlorination
- Aeration
- Disinfection
- Coagulation
- Flocculation
- Slow Sand Filtration
Filtration
Dual Media Filters : These filters work on the principal of depth filtration. The principal media in these filters is quartz grade sand and anthracite. Other supporting media include pebbles of various sizes, crushed gravel and silex. The major advantage of this type of filters is that anthracite which provides for coarse filtration is lighter than filtering sand. Hence on stage of coarse filtration takes place on the anthracite bed and the next stage takes place on the sand bed. Thus depth filtration is achieved. Since both media (viz sand and anthracite) are employed to their capacities the dirt loading capacity of these filters is twice that of Pressure sand filters.
Activated Carbon Filters : The principal media in these filters is activated carbon. Other supporting media include pebbles of various sizes, crushed gravel and silex. The activated carbon is a highly porous media. This property of carbon allows it to adsorb the free chlorine in raw water. Also organic matter present in colloidal form is adsorbed in these pores. Thus odour emanating from raw water on account of these colloids is reduced. The activated carbon present in the standard range has an iodine value of 450. This carbon is also available in iodine values of 600, 900 and 1100.
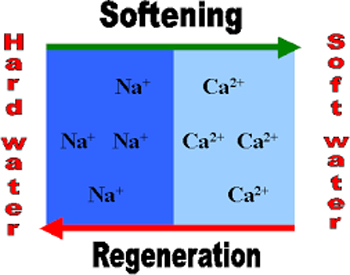
Water Softening Systems : Hardness in water is caused by certain salts. The main hardness causing ions are Calcium (Ca2+), Magnesium (Mg2+) and Bicarbonate (HCO3-).
These ions or minerals are normally addressed as scale in the water causing scaling of pipes and equipment in drinking water and process water systems.
Softening units offer a water purification solution for hard water and lime scale removal.
Demineralization Process(DM Plant) : Demineralization Water Treatment is a physical process. Ion exchange resins are specially manufactured which help to replace the mineral salts in water. There are two types of resins - anion exchange and cation exchange resins. The former resins release hydroxyl ions which are usually negatively charged ions. The cation resins release hydrogen ions which are usually positively charged ions.
Ions found in water :
These are usually metals.
- Iron
- Calcium
- Magnesium
- Copper
- Sodium
- Potassium
These are usually non-metals.
- Chloride
- Carbonate
- Sulphate
- Bicarbonate
- Nitrate
RO PLANT :
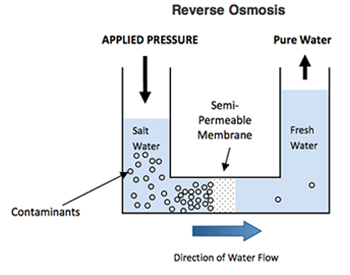
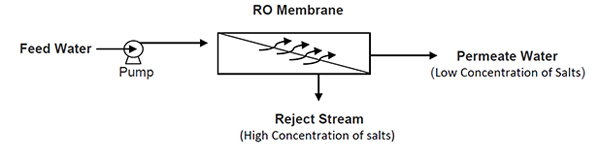
Reverse Osmosis, commonly referred as RO, is a process where water is demineralised by flowing under pressure through a semi-permeable membrane.
How does reverse osmosis work?
In practice, reverse osmosis is applied as a crossflow filtration process.
A high pressure pump is used to increase the pressure on the salt side of the RO and force the water to flow across the semi-permeable membrane., leaving most part (approximately 95%-99%) of the dissolves salts behind the stream.
Within the membrane system, the feed water will be split into a low-saline product, called permeate, and a high saline solution, called concentrate, brine or reject stream.
As the feed water enters the RO membrane under pressure (enough to overcome osmotic pressure), the water molecules pass through a semi-permeable membrane and the salts and other contaminants are not allowed to pass and are discharged through the concentrate stream, which goes to drain or can be fed back (totally or partially) into the feed water stream to be recycled through the RO system to save water or to solve hydraulic issues in the system.
Sewage Treatment Plant :
Sewage treatment refers to the process of removing contaminants, micro-organisms and other types of pollutants from wastewater in fluent. The main objective of sewage treatment is to produce an effluent (treated waste water) and a solid waste/sludge suitable for discharge into the natural environment.
Sewage is water that is discharged after residences, institutions, hospitals, industrial and commercial use.
Majorly, four methods of sewage water treatment are followed - physical, biological, chemical, and sludge water treatment. By following these methods, the wastewater is disinfected from all the sewage materials and converted into treated water that is safe for both human usage and the environment.
There are three main stages of the wastewater treatment process, aptly known as primary, secondary and tertiary water treatment.
Technologies Used :
- ASP: Activated Sludge Process.
- MBBR: Moving Bed Bio reactor.
- SAFF: Submerged aerated Fixed Film.
- SBR: Sequential Bioreactor.
- MBR: Membrane Bio Reactor.
Ultrafiltration System :
Membrane Technology Ultrafiltration (UF) is a water purification process in which water is forced through a semipermeable membrane. Suspended solids and high-molecular-weight solutes remain on one side of the membrane, the retentate side, while water and low-molecular-weight solutes filter through the membrane to the permeate side Ultrafiltration is used for the separation of suspended solids, colloids, bacteria and virus. This technique uses membranes with pore size between 1-100nm.
TECHNIQUE |
MWCO* (Da) |
|
Microfiltration |
>105 |
|
Ultrafiltration |
103-105 |
|
Nano filtration |
102M-104 |
|
Reverse osmosis |
102 |
* MWCO = molecular weight cut-off There are 4 membranes geometries :
- Spiral wound module: this design tries to maximize surface area in a minimum amount of space. It is the less expensive but more sensitive to pollution due to its manufacturing process. It consists of consecutive layers of large membrane and support material in an envelope type design rolled up around a perforated steel tube.
- Plate and frame module: it is normally used for bad quality water. They are set up with a stack of membranes and support plates.
- Tubular membrane: Generally used for viscous or bad quality fluids. These modules do not need a preliminary pre-treatment of the water. As the feed solution flows through the membrane core, the permeate passes through the membrane and is collected in the tubular housing.The main drawback is that the system is not very compact and has a high cost per m2 installed and it is not very compact. Diameter's tube is generally between 4 and 25mm.
- Hollow fiber membrane: The modules contain several small (0.6 to 2 mm diameter) tubes or fibers. As the feed solution flows through the open cores of the fibers, the permeate is collected in the cartridge area surrounding the fibers. It can carry out the filtration in two ways, either "inside-out" or "outside-in" Comparison between the different types of geometry (Source: Water Treatment Handbook, Degremont Suez, 7th edition) :
|
Tubular |
Hollow Fiber |
Plate and Frame |
Spiral Wound |
|
Reverse Osmosis, Nanofiltration |
yes |
yes |
yes |
>95% |
|
Ultrafiltration, Microfiltration |
yes |
>95% |
yes |
yes |
|
Cleaning Ease |
+ |
+++ |
- |
+ |
|
Pre-treatment Need |
+++ |
+ |
+ |
- |
|
Recovery Rate |
+ |
+++ |
+ |
++ |
|
Module Size |
- |
++ |
+ |
++ |
|
Reverse osmosis |
- |
+++ |
+ |
+++ |
There are two ultrafiltration module configurations:
- Pressurized System or Pressure-Vessel Configuration
- Immersed System
Application Area :
- Residential Complexes
- Hospitals
- Colleges
- Restaurants
- Car Washes
- Food Industries
- Laundry
- Textile Industries
- Mall
- Cooling Tower make up
- ow Pressure Boiler
- Process Industries
- Potable Water
- Offices
- Housing Colonies
- Packaged Drinking Water
- Food & Beverages
- Hospitals
- Pharmaceuticals
- Power Generation Industries
- Petrochemical Industries
- Fertilizers
- Boiler Feed
- Distillery
- Paint Industry
- Chemical Industries
- Power Plant
- Automobile Industries
- Rubber Industries